While various denominations have established policies regarding women’s roles, the number of women serving in religious leadership capacities has surged in recent decades.
According to research conducted by theologian Eileen Campbell-Reed, 20.7% of American clergy were women as of 2016 — up from 2.3% in 1960.
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America, which represents 4 million members, reported in 2022 that 40% of its pastors were women. In the Assemblies of God, 27.6% of its ministers currently are women.
The Rev. Dr. Kamilah Hall Sharp, who is affiliated with the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), exemplifies a growing trend among women embracing roles as congregational leaders. Even as some question whether — and how — they should lead, women like Hall Sharp are pursuing alternative pathways to their religious calling.
Hall Sharp, along with the Rev. Dr. Irie Lynne Session, co-founded The Gathering, a womanist church in Dallas. The two ordained ministers planted the church in the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) denomination, after determining that they could fill a void by bringing to the forefront Black women’s voices. On its website, The Gathering describes its context this way: “As more preachers, pastors and ministers of the word intentionally do the deeper exegetical work of interrogating the sacred biblical texts to raise up the muted voices of women, the theological landscape for womanism continues to expand.”
“We obviously still see women who are having to fight to be in spaces and to be affirmed in spaces,” said Hall Sharp, who also is the director of the Doctor of Ministry in Public Ministry Program at Chicago Theological Seminary. “But I also see a trend in which women are welcomed and starting to create their own tables. My church is an example of creating your own table — within a denominational setting.”
Hall Sharp, a former practicing attorney, pursued a theological degree because she felt a call to ministry. After earning her master of divinity at Memphis Theological Seminary, she moved to Texas to pursue a doctorate in biblical interpretation with a focus in Hebrew Bible at Brite Divinity School.
Despite her credentials, she encountered roadblocks. “In Texas, there aren’t a lot of spaces for women,” Hall Sharp said. “I struggled with finding a church home for a while.”
As a result, Hall Sharp and Session started brainstorming about creating a new space where people could experience womanist preaching. “It eventually evolved into a church. Because we’re both ordained in Disciples of Christ, it became a new church of Disciples of Christ.”
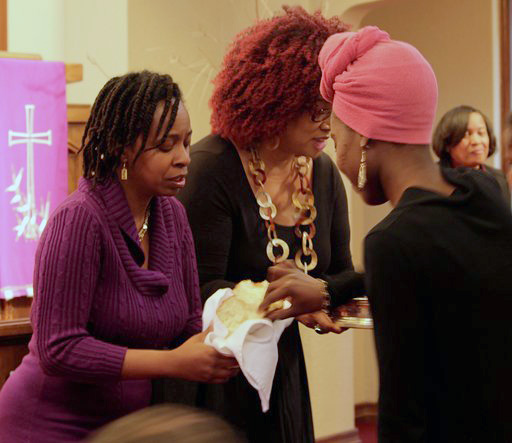
The two didn’t initially consider planting a church. “As it is for a lot of women, we started the church out of necessity,” said Hall Sharp, who co-authored the book “The Gathering, A Womanist Church: Origins, Stories, Sermons and Litanies.”
“We didn’t have support from our denomination to start the church. And even when we did get financial support, it wasn’t a lot,” she said.
The Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), which has ordained women since the 1880s, recently appointed the Rev. Teresa Hord Owens to a second term as general minister and president in the United States and Canada — the first person of color and second woman to lead the denomination — but women continue to have fewer opportunities than men, Hall Sharp said.
In her experience, she said, women are typically assigned to or hired at churches that aren’t able to pay as much. “As a result, they’re never able to really be a full-time pastor,” Hall Sharp said. “So many women in ministry have to have other jobs, because they typically don’t get the churches with all the resources.”
Hall Sharp’s experience highlights a common theme of continued inequity among women taking on leadership roles, according to Campbell-Reed, a visiting associate professor at Union Theological Seminary in New York and co-director of the Learning Pastoral Imagination Project.
“Many women are doing great, but there’s still controversy and conflict everywhere they go,” Campbell-Reed said. “We still have inequities in pay and disparities about where women can start and the extent to which they can grow. They’re still more likely to get associate roles or roles in very small churches.”
Rabbi Dr. Rachel Mikva, a professor of Jewish studies and the senior faculty fellow of the InterReligious Institute at Chicago Theological Seminary, has observed similar patterns in rabbinic roles. She noted that women are leading two of the major rabbinic seminaries. In 2020, Jewish Theological Seminary appointed Shuly Rubin Schwartz as its new chancellor — the first woman to hold the role since its founding in 1886 — and Rabbi Sharon Cohen Anisfeld became president of Hebrew College in 2018.
Those types of developments obviously have been helped by women’s movements across the United States, Mikva said. “However, it’s not without bumps. Women have been moving into rabbinic positions, but not every community was immediately ready to hire a woman to be the rabbi,” she said.
While planting The Gathering was challenging, Hall Sharp said, the rewards were worth it. She said one of the major benefits was providing other women a platform to develop. “It’s difficult to create new spaces, because you don’t necessarily get the financial support that you see others getting,” she said. “But it’s been very rewarding, because people have found a place where they can feel whole; they can come as their complete selves.”
Hall Sharp envisions a future in which women are embraced in their roles as leaders. “I hope to see more women be OK with who they are, to be able to walk authentically, and to see more spaces where they are affirmed and appreciated and their leadership is respected,” she said.